anatomical Landmarks
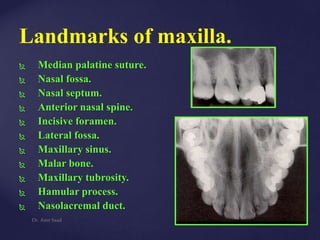
- 1. Landmarks of maxilla. Median palatine suture. Nasal fossa. Nasal septum. Anterior nasal spine. Incisive foramen. Lateral fossa. Maxillary sinus. Malar bone. Maxillary tubrosity. Hamular process. Nasolacremal duct. Dr. Amr Saad
- 2. 1- Median palatine suture: Appears as a vertically oriented radiolucent line in true image projections through the midline. Usually prominent between the two central incisor roots at young individuals. Dr. Amr Saad
- 3. 1- Nasal septum: (17)Appear as a radio-opaque line separates the two nasal fossa in the midline. 2- Anterior nasal spine(16) Appears as a v-shaped radio-opaque structure in the midline above the incisive foramen. 3- Incisive foramen:(12) or the anterior palatine fossa, it usually appears as a prominent radiolucent area above/or between the roots of two central incisors. It usually appears as a rounded or oval in shape doesn’t not exceed 6mm in diameter. Dr. Amr Saad
- 4. Anterior nasal spine Dr. Amr Saad Nasal cavities Nasal septum Median palatine suture
- 5. Dr. Amr Saad Maxillary anterior region Nasal septum Nasal fossa Nasal spine Incisive foramen Nose Median palatine suture
- 6. Dr. Amr Saad e f a = nasal septum c = nasal fossa d = anterior nasal spine e = incisive foramen f = median palatal suture a d c facial view palatal view
- 7. Dr. Amr Saad Nasal septum facial view
- 8. Dr. Amr Saad Nasal fossa facial view
- 9. Dr. Amr Saad Incisive foramen palatal view
- 10. Dr. Amr Saad Median palatal suture palatal view
- 11. Dr. Amr Saad Soft tissue of the nose
- 12. Dr. Amr Saad Red arrow points to Periapical lesion (post- endo) a d b Red arrows = lip line
- 13. Dr. Amr Saad Red arrow = mesiodens (supernumerary tooth) d f Blue arrow = chronic periapical periodontitis. Tooth # 9 is non-vital (trauma) and needs endo.
- 14. Dr. Amr Saad The red arrows point to the soft tissue of the nose. The green arrows identify the lip line.
- 15. 5-Maxillary sinus: The maxillary sinus with its thin bony walls, its thin mucosa, and its vast air space, produce an extremely dark image deep to the maxillary teeth. Its outlines, particularly its floor, are clearly delineated by delicate radiopaque lines. Dr. Amr Saad
- 16. 1-Body of zygoma 6-Apices of roots 7-floor of the sinus 8-Septum of the sinus Dr. Amr Saad Notice the well-demarcated RL area related to upper 5
- 17. In general the floor of the sinus is approximately coincidental with the location of the apices of the roots of the upper teeth,(bicuspids and first two molars). But there is often as much as two or even three millimeters of maxillary bone between the root ends and sinus floor. Dr. Amr Saad
- 18. In other cases the sinus floor dips so deeply between the roots of the maxillary teeth that the latter appear to project into it for as much as one half of their length. Dr. Amr Saad
- 19. Dr. Amr Saad Pneumatization. Expansion of sinus wall into surrounding bone, usually in areas where teeth have been lost prematurely. Increases with age.
- 20. Dr. Amr Saad Maxillary Canine Floor of nasal fossa Maxillary sinus Lateral fossa Nose
- 21. Dr. Amr Saad a = floor of nasal fossa b = maxillary sinus c = lateral fossa (a & b form inverted Y) a c b a c b facial view
- 22. Dr. Amr Saad Floor of nasal fossa (red arrows) and anterior border of maxillary sinus (blue arrows), forming the inverted (upside down) Y. facial view
- 23. Dr. Amr Saad Lateral fossa. The radiolucency results from a depression above and posterior to the lateral incisor. To help rule out pathology, look for an intact lamina dura surrounding the adjacent teeth. facial view
- 24. Dr. Amr Saad The maxillary sinus surrounds the root of the canine, which may be misinterpreted as pathology. The black arrows indicate the floor of the nasal fossa. The maxillary sinus (red arrows) has pneumatized between the 2nd premolar and first molar
- 25. Dr. Amr Saad Zygomatic process Sinus septum Maxillary sinus Maxillary Premolar region
- 26. Dr. Amr Saad a = malar process c = sinus septum d = maxillary sinus a c d d c a facial view
- 27. Dr. Amr Saad Malar (zygomatic) process. U or j-shaped radiopacity, often superimposed over the roots of the molars, especially when using the bisecting-angle technique. The red arrows define the lower border of the zygomatic bone. facial view
- 28. 6- Malar bone: Or the zygomatic process. The inferior portion of the malar bone appears as a Radiopaque u-shaped structure related to the roots of the first maxillary molar. It represents the attachment of the zygomatic bone to the maxilla. 7- Maxillary tuberosity: Appears as a Radiopaque structure that extends distally and upward from posterior to maxillary sinus. It represents the end of maxilla. Dr. Amr Saad
- 29. 9- Hamular process: It is a bony spine projecting from the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. It appears as a Radiopaque spine that recorded on radiographs distal to the tuberosity of the maxilla and extends downward. 10- Coronoid process of the mandible: Appears as a triangular Radiopaque structure projected into the same general area of maxillary Periapical film projections distally to the maxillary teeth. Dr. Amr Saad
- 30. Dr. Amr Saad Maxillary Molar Region Maxillary sinus Zygoma Pterygoid plate Hamular process Coronoid process Maxillary tuberosity
- 31. Dr. Amr Saad g d a e f a = maxillary tuberosity* e = zygoma (dotted lines) b = coronoid process f = maxillary sinus c = hamular process g = sinus recess d = pterygoid plates * image of impacted third molar superimposed c facial view d b a e c f g
- 32. Dr. Amr Saad Maxillary Tuberosity. The rounded elevation located at the posterior aspect of both sides of the maxilla. Aids in the retention of dentures. facial view
- 33. Dr. Amr Saad Coronoid process. A mandibular structure sometimes seen on the maxillary molar periapical film when using the bisecting angle technique with finger retention (The mouth is opened wide, moving the coronoid down and forward). Note the supernumerary molar. facial view
- 34. Dr. Amr Saad Hamular process (black arrows) and pterygoid plates (purple arrows). The hamular process is an extension of the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone, positioned just posterior to the maxillary tuberosity. facial view
- 35. Dr. Amr Saad The zygomatic process (green arrows) is a prominent U-shaped rationality. Normally the zygomatic bone posterior to this is very dense and Radiopaque. In this patient, however, the maxillary sinus has expanded into the zygomatic bone and makes the area more radiolucent (red arrows). The coronoid process (orange arrow), the pterygoid plates (blue arrows) and the maxillary tuberosity (pink arrows) are also identified.
- 36. Dr. Amr Saad 1- Floor of nasal cavity, 2- Laterobasal border of nasal cavity, 3- Maxillary sinus, 4- Floor of the sinus, 5- Septum dividing the sinus, 11- Alveolar crest.
- 37. Dr. Amr Saad 1- Zygomatic process, 2- body of zygoma, 6- Maxillary sinus, 7- floor of the sinus, 9- Max. tuberosity, 10- alveolar crest, 11- Coronoid process.
- 38. 11- Nasolacrimal duct: It almost seen in occlusal view of the maxilla as a round radiolucent area superimposed on the posterior region of the hard palate. Dr. Amr Saad
- 39. Dr. Amr Saad 1-Anterior nasal spine, 2-Boundries of nasal cavity, 3-Nasal septum, 4-Nasal cavity, 5-Nasal bone, 6-Maxilary sinus, 7-Zygomatic process, 8-Nasolacremal duct.
- 40. Panoramic view 1-Nasal septum, 2-Nasal cavity, 3-Orbit, 4-Border of nasal cavity, 6-Maxillary sinus, 8-Incisive foramen, 9-Anterior nasal spine Dr. Amr Saad
- 41. 1- Nasal septum, 7- Maxillary sinus, 8-Orbit, 9-Nasal bone, 10-Anterior nasal spine, 11-Border of nasal cavity, 13- Shadow of hyoid bone. Dr. Amr Saad
- 42. Dr. Amr Saad Landmarks of Mandible.
- 43. Landmarks of Mandible. Lingual foramen Genial tubercles. Mental ridge. Mental foramen. Mental fossa. External oblique line. Internal oblique line. Mylohyoid line or ridge. Mandibular foramen. Inferior dental canal. Submandibular gland fossa. Interdental nutrient canals. Pharyngeal space. Dr. Amr Saad
- 44. Lingual foramen: Is set in the midline deep to the root apices of the anterior teeth. It appears as a small radiolucent dot at the symphysis area. It usually surrounded with a Radiopaque structure. Dr. Amr Saad
- 45. Genial Tubercles: Or the superior and inferior mental spines. They are four in number located toward the inferiolingual border of the mandible and are mostly 2 on each side of the midline, although in some instances they coalesce as a single radiopaque outcrop of the mandible. They appear as a radiopaque circle that surrounds the lingual foramen, just below the apices of the incisors. Anatomically genyoglossal muscle attached to the superior two while the genyohyoid muscle attached to the inferior two. Dr. Amr Saad
- 46. Mental ridge: It is a bony prominence found on the labial aspect of the mandible near its inferior border and extended from the premolar region to the symphysis area on which it takes an upward turn as it approach it. It appears as a radiopaque line below the apices of anterior teeth. Dr. Amr Saad
- 47. Dr. Amr Saad Mandibular Incisors region Mental ridge Genial tubercles Lingual foramen Mental fossa
- 48. Dr. Amr Saad b = genial tubercles a = lingual foramen c = mental ridge d = mental fossa a b c d facial view lingual view
- 49. Dr. Amr Saad Lingual foramen. Radiolucent “hole” in center of genial tubercles. Lingual nutrient vessels pass through this foramen. lingual view
- 50. Dr. Amr Saad Genial tubercles. Radiopaque area in the midline, midway between the inferior border of the mandible and the apices of the incisors. Serve as attachments for the genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles. May have radiolucent hole in center (lingual foramen), but not on this film. Note double rooted canine (red arrows). lingual view
- 51. Dr. Amr Saad Mental ridge. facial view
- 52. Dr. Amr Saad Mental fossa. This represents a depression on the labial aspect of the mandible overlying the roots of the incisors. The resulting radiolucency may be mistaken for pathology. facial view
- 53. Dr. Amr Saad The orange arrows above identify nutrient canals. They are most often seen in older persons with thin bone, and in those with high blood pressure or advanced periodontitis. Nutrient canals
- 54. Dr. Amr Saad Mental foramen(3) It appears as a radiolucent ill-defined area between the apices of the bicuspids. It represent the anterior terminates of the mandibular canal.
- 55. Dr. Amr Saad 6- Caries. 7- Prepared cavity. 8- Enostosis. 9- Mental foramen.
- 56. Mental Fossa (6): It is a slight depression in the bone one the labial aspect of the mandible. It appears as a faint radiolucent structure related to anterior area. Dr. Amr Saad Notice: 7 is cervical burnout
- 57. Dr. Amr Saad Mandibular Premolar region a = mylohyoid ridge b = mandibular canal c = submandibular gland fossa d = mental foramen
- 58. Dr. Amr Saad c b = mandibular canal d = mental foramen a = mylohyoid ridge (internal oblique) c = submandibular gland fossa facial view lingual view c a d d b
- 59. Dr. Amr Saad Mental foramen. Usually located midway between the upper and lower borders of the body of the mandible, in the area of the premolars. May mimic pathology if superimposed over the apex of one of the premolars. facial view
- 60. Dr. Amr Saad Mandibular Molar region a = external oblique ridge b = mylohyoid ridge c = mandibular canal d = submandibular gland fossa
- 61. Dr. Amr Saad facial view lingual view b c a b a = external oblique ridge c = mandibular canal b = mylohyoid ridge d = submandibular gland fossa d d
- 62. External oblique line:(6) It is a Radiopaque line extending from anterior border of the ramus of the mandible and descends to the third molar area. 7-Internal oblique line, 7-Mylohyoid line, 9-Mandibular canal, Dr. Amr Saad
- 63. Dr. Amr Saad External oblique ridge. A continuation of the anterior border of the ramus, passing downward and forward on the buccal side of the mandible. It appears as a radiopaque line which usually ends anteriorly in the area of the first molar. Serves as an attachment of the buccinator muscle. (The red arrows point to the mylohyoid ridge). facial view
- 64. Internal oblique line(6): It appears as a Radiopaque line descends downward and forward from Coronoid process; in a more horizontal position; stop at the third molar area or become continuous with the Mylohyoid line. Its place below the external oblique line. Dr. Amr Saad
- 65. Mylohyoid line or ridge(7) It is a Radiopaque line below the external oblique line and it is the anterior continuity of the internal oblique line. It extend downward and forward from the ramus of the mandible to the bicuspid areas. Dr. Amr Saad
- 66. Dr. Amr Saad Mylohyoid ridge (internal oblique). Located on the lingual surface of the mandible, extending from the third molar area to the premolar region. Serves as the attachment of the mylohyoid muscle. lingual view
- 67. Inferior dental canal; (9,2), Mandibular canal, or inferior alveolar canal. Its characteristic image is therefore likely to be a radiolucent passage along the mandible just deep to the roots of the teeth, terminating at the mental foramen and bounded by Radiopaque margins representing the walls of thin cortical bone bounding the canal. Dr. Amr Saad
- 68. Dr. Amr Saad facial view Mandibular (inferior alveolar) canal. Arises at the mandibular foramen on the lingual side of the ramus and passes downward and forward, moving from the lingual side of the mandible in the third molar region to the buccal side of the mandible in the premolar region. Contains the inferior alveolar nerve and vessels.
- 69. Submandibular gland fossa(4): It is a depression on the lingual aspect of the mandible on which submandibular glands are present. It appears as a zone of radiolucency below the lower molars. Dr. Amr Saad
- 70. Dr. Amr Saad lingual view Submandibular gland fossa. A depression on the lingual side of the mandible below the mylohyoid ridge. The submandibular gland is located in this region. Due to the thinness of bone, the area being very radiolucent. The fact that it occurs bilaterally helps to differentiate it from pathology.
- 71. Dr. Amr Saad a b c d d a = external oblique ridge b = mylohyoid ridge c = mandibular canal d = submandibular gland fossa
- 72. Dr. Amr Saad The external oblique ridge (red arrows) and the mylohyoid ridge (blue arrows) usually run parallel with each other, with the external oblique ridge always being higher on the film.
- 73. Dr. Amr Saad The mandibular canal (red arrows identify inferior border of canal) usually runs very close to the roots of the molars. Note the extreme dilaceration of the roots of the third molar (green arrow). The film at right shows “kissing” impactions located at the superior border of the canal.
- 74. Dr. Amr Saad 9-buccal & lingual compact bone 10-genial tubercle 11-Mental foramen
- 75. Dr. Amr Saad 1-Inferior border of the mandible 4-Mental fovea 2-Mental protuberance 5- Mental foramen 3-Digastric fovea 12-Radiolucency created by the lip
- 76. Dr. Amr Saad 1,2- compact bone of mandible 4- mental fovea, 5-mental foramen, 6-mylohyoid line, 7-submandibular gland fossa, 8-hyoid bone, 12-lip radiolucency
- 77. Dr. Amr Saad 1-external oblique line, 3-mental foramen, 4-madibular canal, 5-inferior border of the mandible.
- 78. Edentulous patient 1-mandibular foramen, 2-coronoid process, 3-zygomatic arch, 4-cervical vertebra, 7-mental foramen, 8-mandibular canal Dr. Amr Saad
- 79. Thank You Dr. Amr Saad
